※ 100% 완벽한 코드는 아닙니다! 참고용으로 봐주세요. ※
Supplemental Page Table - Revisit
vm.c
supplemental_page_table_copy
해당 함수는 fork과정에서 부모의 주소를 자식에게 복사해주는 기능을 합니다.
부모의 주소 공간을 src라 지칭하고, 자식의 주소 공간을 dst라고 지칭합니다.
src와 dst는 지칭하는 대명사라고 생각하면되고, src에는 현재 스레드의 spt가 들어갈 것입니다.
해당 함수를 구현하는 중에 unint 타입부분 확인에서 트러블 슈팅이 있었고 다음은 수정본입니다. 6월8일 TIL을 통해 트러블 슈팅 과정을 확인가능합니다.
bool
supplemental_page_table_copy (struct supplemental_page_table *dst UNUSED,
struct supplemental_page_table *src UNUSED) {
// src의 해시 테이블 순회 준비
struct hash_iterator i;
hash_first(&i, &src -> spt_hash); // spt가 해쉬에 있음. first로 첫번째 버킷 지정
// 모든 page를 하나씩 순회(모든 버킷)
while (hash_next(&i)) {
struct page *src_page = hash_entry(hash_cur(&i), struct page, hash_elem);
// 공통 메타데이터 추출
void *va = src_page -> va;
enum vm_type type = page_get_type(src_page); // 부모 실제 타입 추출
bool writable = src_page -> writable;
// unint 타입인지 확인
if (src_page->operations->type == VM_UNINIT) { // fork-read를 위한 수정
// init 함수와 aux 복사 (지연로딩)
struct uninit_page *uninit = &src_page -> uninit;
vm_initializer *init = uninit -> init;
void *aux = uninit -> aux;
// dst에 등록
vm_alloc_page_with_initializer(type, va, writable, init, aux);
}
// 초기화된 페이지라면
else {
// dst에도 동일한 페이지를 생성한다.
vm_alloc_page_with_initializer(type, va, writable, NULL, NULL);
// dst 페이지 가져와서 claim 한다.
struct page *dst_page = spt_find_page(dst, va);
vm_claim_page(va);
// printf("dstpage: %p\n", dst_page -> frame -> kva);
// printf("srcpage: %p\n", src_page -> frame -> kva);
// 실제 프레임 데이터를 복사
memcpy(dst_page -> frame -> kva, src_page -> frame -> kva, PGSIZE); // 목적지, 출발지, 사이즈 순이다.
}
// 기타 속성을 복사
if (src_page -> is_stack)
spt_find_page(dst, va) -> is_stack = true;
}
return true;
}코드 구현에 앞서 어느정도의 용어를 알아보면 좋다.
용어 인덱스
| 용어 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| uninit page | 아직 물리 메모리에 로드되지 않았고, 실제 데이터도 없는 페이지. 단지 “어떻게 로딩할지”에 대한 정보만 가진 상태 |
| lazy loading | 페이지에 실제로 접근(Page Fault)할 때까지, 물리 메모리 할당과 파일 로딩을 미루는 기법 |
| uninit -> anon/file/etc. | 나중에 해당 페이지가 접근되면, uninit->page_initializer()를 통해 진짜 페이지로 변신함 |
supplemental_page_table_kill
포크 완료 후에 사용이 완료된 자식 페이지를 해제하고 쓰기위해 쓰입니다. 자원해제 같은겁니다. spt 테이블을 모두 파괴하고, 그 안에 있는 페이들을 해제하기 위해 page_destory 라는 함수가 필요합니다. page_destory는 페이지 매핑을 해제하고 프레임이 있다면 해제합니다.
→ 해당 함수는 코어타임에서 어느정도 흐름을 파악했고, 코드도 그리 어렵지 않아서 비교적 빨리 했습니다.
void page_destroy (struct hash_elem *e, void *aux) {
struct page *src_page = hash_entry(e, struct page, hash_elem);
// 페이지 매핑 해제 & 프레임이 있다면 해제
vm_dealloc_page(src_page);
}
/* Free the resource hold by the supplemental page table */
// 보충 페이지 테이블에서 리소스 보류를 해제합니다.
void
supplemental_page_table_kill (struct supplemental_page_table *spt UNUSED) {
/* TODO: Destroy all the supplemental_page_table hold by thread and
* TODO: writeback all the modified contents to the storage. */
// 스레드가 보유한 supplemental_page_table을 모두 파괴하고 수정된 내용을 모두 저장소에 다시 쓰게 구현하세요.
hash_clear(&spt -> spt_hash, page_destroy); // 그 안에 있는 페이지들 해제(page_destroy), 해시들도 해제,
// hash_destroy(&spt -> spt_hash, page_destroy); // hash_destory로 하면 문제가 생긴다. 아마 process_cleanup 두번하는 문제도 있고, 다양하다.
}완료를 한다면, fork가 가능하게되므로 추가로 13개의 테스트 케이스를 통과할 수 있습니다.
... 일부 생략
pass tests/userprog/fork-once
pass tests/userprog/fork-multiple
pass tests/userprog/fork-recursive
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-read
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-close
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-boundary
pass tests/userprog/exec-once
pass tests/userprog/exec-arg
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-boundary
pass tests/userprog/exec-missing
pass tests/userprog/exec-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-read
pass tests/userprog/wait-simple
pass tests/userprog/wait-twice
pass tests/userprog/wait-killed
pass tests/userprog/wait-bad-pid
pass tests/userprog/multi-recurse
pass tests/userprog/multi-child-fd
pass tests/userprog/rox-simple
pass tests/userprog/rox-child
pass tests/userprog/rox-multichild
pass tests/userprog/bad-read
pass tests/userprog/bad-write
pass tests/userprog/bad-read2
pass tests/userprog/bad-write2
pass tests/userprog/bad-jump
pass tests/userprog/bad-jump2
FAIL tests/vm/pt-grow-stack
pass tests/vm/pt-grow-bad
FAIL tests/vm/pt-big-stk-obj
pass tests/vm/pt-bad-addr
pass tests/vm/pt-bad-read
pass tests/vm/pt-write-code
FAIL tests/vm/pt-write-code2
FAIL tests/vm/pt-grow-stk-sc
pass tests/vm/page-linear
pass tests/vm/page-parallel
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-seq
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-par
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-stk
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-mm
pass tests/vm/page-shuffle
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-read
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-close
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-unmap
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-overlap
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-twice
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-write
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-ro
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-exit
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-shuffle
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-clean
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-inherit
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-misalign
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-null
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-code
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-data
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-stk
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-remove
pass tests/vm/mmap-zero
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd2
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd3
pass tests/vm/mmap-zero-len
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-off
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-bad-off
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-kernel
FAIL tests/vm/lazy-file
pass tests/vm/lazy-anon
FAIL tests/vm/swap-file
FAIL tests/vm/swap-anon
FAIL tests/vm/swap-iter
FAIL tests/vm/swap-fork
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-create
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-full
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-random
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-block
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-random
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-create
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-full
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-random
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-block
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-read
pass tests/filesys/base/syn-remove
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-write
pass tests/threads/alarm-single
pass tests/threads/alarm-multiple
pass tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
pass tests/threads/alarm-priority
pass tests/threads/alarm-zero
pass tests/threads/alarm-negative
pass tests/threads/priority-change
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-one
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
pass tests/threads/priority-fifo
pass tests/threads/priority-preempt
pass tests/threads/priority-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-condvar
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
FAIL tests/vm/cow/cow-simple
41 of 141 tests failed.Page Cleanup
Gitbook에 있는 Page Cleanup 부분은 나중에 구현해야할 때, 추가로 건드리면 된다고 합니다. 그러므로 바로 Stack Growth에 들어가보도록 하겠습니다.
Stack Growth
Stack Growth는 사용자 프로그램이 스택 크기를 초과해서 더 많은 공간을 사용하려고 할 때, 운영체제가 자동으로 새로운 페이지를 할당해 스택을 확장해주는 기능입니다. Pintos에서는 이 기능을 Page Fault와 연계해서 구현합니다.
vm.c
vm_try_handle_fault
먼저 vm_try_handle_fault 함수를 수정해줘야한다. 왜냐하면 스택 자동확장이 필요한 시기에 확장을 시도해야하기 때문입니다. 즉, 스택 증가를 식별해줍니다. 케이스1과 2가 정상적으로 실행된다면 페이지 적재를 수행합니다.
bool
vm_try_handle_fault (struct intr_frame *f UNUSED, void *addr UNUSED,
bool user UNUSED, bool write UNUSED, bool not_present UNUSED) {
struct supplemental_page_table *spt UNUSED = &thread_current ()->spt;
struct page *page = spt_find_page(spt, addr); /* valid address인지 확인 */
void *user_rsp = thread_current()->user_rsp; // 시스템 콜 중이라도 유저 %rsp
// void *user_rsp = user ? thread_current()->user_rsp : f->rsp;
void *va = pg_round_down(addr); // 주소를 정렬에 맞춰준다.
/* TODO: Validate the fault */
/* TODO: Your code goes here */
// case 1: page가 없음 → stack growth 고려
// 스택 자동확장이 필요한 상황일 때, vm_stack_growth 함수로 확장해줍니다.
if(page == NULL) {
// 유저 모드에서 발생한 폴트만 처리, 유저 스택 포인터 바로 아래에 접근할 시 허용, 접근한 주소가 전체 유저 스택 범위 안에 있는지 확인. -> 모든 조건일시 스택 확장
// 스택확장 부분이 왜 if문에 있는지 의아할 수 있는데, 이는 스택확장이 무조건 성공하지 않으므로 실패시 spt_find_page를 실행하지 않도록 방지한다.
if (is_user_vaddr(addr) && user && addr >= f->rsp - 32 && addr < USER_STACK && vm_stack_growth(addr)) {
page = spt_find_page(spt, addr); // addr이 현재 스택 영역 바로 아래에 접근한 경우에만 새 페이지를 할당
}
else
return false;
}
// case 2: 접근 권한 확인 (write 접근인데 read-only면 실패)
if (write && !page->writable) // 쓰기 접근인데 페이지가 읽기 전용이라면, false 반환
return false;
// 페이지 적재 (uninit이든 아니든 모두 처리)
return vm_do_claim_page (page);
}vm_stack_growth
놀랍게도 다음과 같이 구현하면 테스트 케이스가 통과된다. 페이지 폴트에서 지정해준 조건(유저 주소, 유저 영역 등) 스택 확장 조건에 맞으면, 해당 함수로 확장을 시도합니다.
// 스택을 키웁니다.
static bool
vm_stack_growth (void *addr UNUSED) {
struct thread *t = thread_current();
void *va = pg_round_down(addr); // 주소를 정렬에 맞춰준다.
// 실제로 할당 요청
return vm_alloc_page(VM_ANON | VM_MARKER_0, va, true); // VM_MARKER_0: 스택에서 생성된 익명 페이지를 구별하기 위함
}tests/vm/pt-grow-stack 와 tests/vm/pt-big-stk-obj 두가지 테스트 케이스가 통과합니다. 좀 더 개선한다면, 다른 테스트 케이스도 통과할 것입니다. (예를 들어 기존의 rsp 포인터를 저장하는 등)
... 일부 생략
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-read
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-close
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-boundary
pass tests/userprog/exec-once
pass tests/userprog/exec-arg
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-boundary
pass tests/userprog/exec-missing
pass tests/userprog/exec-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-read
pass tests/userprog/wait-simple
pass tests/userprog/wait-twice
pass tests/userprog/wait-killed
pass tests/userprog/wait-bad-pid
pass tests/userprog/multi-recurse
pass tests/userprog/multi-child-fd
pass tests/userprog/rox-simple
pass tests/userprog/rox-child
pass tests/userprog/rox-multichild
pass tests/userprog/bad-read
pass tests/userprog/bad-write
pass tests/userprog/bad-read2
pass tests/userprog/bad-write2
pass tests/userprog/bad-jump
pass tests/userprog/bad-jump2
pass tests/vm/pt-grow-stack
pass tests/vm/pt-grow-bad
pass tests/vm/pt-big-stk-obj
pass tests/vm/pt-bad-addr
pass tests/vm/pt-bad-read
pass tests/vm/pt-write-code
FAIL tests/vm/pt-write-code2
FAIL tests/vm/pt-grow-stk-sc
pass tests/vm/page-linear
pass tests/vm/page-parallel
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-seq
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-par
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-stk
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-mm
pass tests/vm/page-shuffle
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-read
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-close
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-unmap
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-overlap
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-twice
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-write
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-ro
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-exit
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-shuffle
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-clean
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-inherit
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-misalign
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-null
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-code
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-data
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-stk
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-remove
pass tests/vm/mmap-zero
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd2
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd3
pass tests/vm/mmap-zero-len
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-off
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-bad-off
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-kernel
FAIL tests/vm/lazy-file
pass tests/vm/lazy-anon
FAIL tests/vm/swap-file
FAIL tests/vm/swap-anon
FAIL tests/vm/swap-iter
FAIL tests/vm/swap-fork
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-create
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-full
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-random
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-block
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-random
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-create
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-full
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-random
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-block
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-read
pass tests/filesys/base/syn-remove
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-write
pass tests/threads/alarm-single
pass tests/threads/alarm-multiple
pass tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
pass tests/threads/alarm-priority
pass tests/threads/alarm-zero
pass tests/threads/alarm-negative
pass tests/threads/priority-change
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-one
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
pass tests/threads/priority-fifo
pass tests/threads/priority-preempt
pass tests/threads/priority-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-condvar
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
FAIL tests/vm/cow/cow-simple
39 of 141 tests failed.거의 하루간(6월8일 ~ 9일) 디버깅을 하며 지낸결과 테스트 케이스(tests/vm/pt-grow-bad)를 고작 1개만 추가로 통과했습니다. 시간이 너무 오래걸려 이어서 mmap를 구현해봤습니다.
+++ 추가로 팀원분들의 코드를 트러블 슈팅하여서 mmap 구현시간이 늦어졌습니다. 관련 내용을 확인하시려면 6월9일( 채호형 트러블슈팅), 6월10일(은수 트러블슈팅)을 참고해주세요.
완료된 이후에는 제출을 위한 merge를 진행하였습니다.
Memory Mapped Files
※ 주의! 이번 mmap부터는 완벽하지 않을 수 있으니, 참고하여 구현바랍니다.
이번에는 mmap, munmap 라는 메모리 매핑된 페이지를 구현합니다. 익명 페이지와 다르게 메모리 매핑된 페이지는 파일 기반 매핑입니다. 페이지의 내용은 기존 파일의 데이터를 반영하고, 페이지 폴트가 발생하면 물리적 프레임이 즉시 할당되고 내용이 파일에서 메모리로 복사됩니다. mmap의 매핑이 해제되거나 swap out 되면 변경 사항이 파일에 반영됩니다.
코드는 기윤님 코드 기반으로 작성되었습니다. https://velog.io/@mogiyoon/Pintos-%ED%94%84%EB%A1%9C%EC%A0%9D%ED%8A%B83-%EA%B3%A0%EC%B0%B0%EA%B0%99%EB%8B%A4
file.c
do_mmap
mmap을 수행하는 주요 코드입니다. 이번 mmap은 process.c에 있는 load_segment 함수를 참고하여 작성하면 좋습니다.
// mmap 관련 기능입니다.
void *
do_mmap (void *addr, size_t length, int writable,
struct file *file, off_t offset) {
off_t file_ofs;
//printf("addr: %d, length: %d, writable:%d, file: %d, file_ofs: %d\n", addr, length, writable, file, file_ofs);
void *backup_addr = addr;
addr = pg_round_down(addr);
off_t total_len = file_length(file);
//printf("total_len: %d\n",total_len);
uint32_t read_bytes = total_len - offset;
uint32_t zero_bytes = ROUND_UP(read_bytes, PGSIZE) - read_bytes;
off_t ofs = offset;
uint8_t * upage = addr;
while (read_bytes > 0 || zero_bytes > 0){
size_t page_read_bytes = read_bytes < PGSIZE ? read_bytes : PGSIZE;
size_t page_zero_bytes = PGSIZE - page_read_bytes;
struct mmap_file *mmap = calloc(1, sizeof(struct mmap_file));
mmap -> addr = addr;
// mmap -> length = length;
mmap -> writable = writable;
mmap -> file = file;
mmap -> ofs = ofs;
mmap -> read_bytes = page_read_bytes;
mmap -> zero_bytes = page_zero_bytes;
if(!vm_alloc_page_with_initializer(VM_FILE, addr, writable, lazy_load_mmap, mmap)) {
return false;
}
// vm_alloc_page()
read_bytes -= page_read_bytes;
zero_bytes -= page_zero_bytes;
upage += PGSIZE;
/* file_read를 하지 않기 때문에 수동으로 ofs을 이동시켜줘야 한다. */
ofs += page_read_bytes;
}
return backup_addr;
}물론 위의 mmap구조체를 쓰기 위해서는 상단에 해당 구조체를 선언해줘야합니다.
struct mmap_file {
int mapid;
struct file *file;
void *addr;
size_t length;
int writable;
struct list_elem elem;
off_t ofs;
uint32_t read_bytes;
uint32_t zero_bytes;
};lazy_load_mmap
do_mmap를 위해선 lazy_load_mmap이라는 lazy 페이지를 mmap하는 코드가 필요하게 됩니다. process.c의 lazy_load_segment를 참고하여 다음과 같이 만들어주면 됩니다.
// mmap에서 lazy페이지를 로드한다.
static bool
lazy_load_mmap (struct page *page, void *aux) {
// printf("mmap lazy load\n");
uint8_t* upage = page->va;
uint8_t* kpage = page->frame->kva;
struct mmap_file* mmap = (struct mmap_file*)aux;
struct file* file = mmap -> file;
off_t ofs = mmap -> ofs;
size_t page_read_bytes = mmap -> read_bytes;
size_t page_zero_bytes = mmap -> zero_bytes;
ASSERT ((page_read_bytes + page_zero_bytes) % PGSIZE == 0);
ASSERT (pg_ofs (upage) == 0);
ASSERT (ofs % PGSIZE == 0);
/* Do calculate how to fill this page.
* We will read PAGE_READ_BYTES bytes from FILE
* and zero the final PAGE_ZERO_BYTES bytes. */
/* Load this page. */
if (file_read_at (file, kpage, page_read_bytes, ofs) != (int) page_read_bytes) {
return false;
}
memset (kpage + page_read_bytes, 0, page_zero_bytes);
free(aux);
return true;
}do_munmap
do_munmap() 함수는 do_mmap()을 통해 메모리에 매핑한 파일을 해제(unmap)하는 역할을 합니다.
간단히 말해, mmap()으로 매핑된 가상 주소 영역을 정리하고, 필요한 경우 해당 내용을 디스크 파일에 반영한 뒤, 메모리를 해제하는 것입니다.
void
do_munmap (void *addr) {
struct page *page = NULL;
int count = 0;
while((page = spt_find_page(&thread_current()->spt, addr)) != NULL){
struct container *aux = (struct container *)page->uninit.aux;
if(pml4_is_dirty(thread_current()->pml4, page->va)){
file_write_at(aux->file, page->va, aux->page_read_bytes, aux->ofs);
pml4_set_dirty(thread_current()->pml4, page->va, 0);
}
count++;
//spt_remove_page(thread_current()->spt, page);
pml4_clear_page(thread_current()->pml4, addr);
addr += PGSIZE;
}
}vm.h
다음과 같이 struct 구조체 추가를 해줍니다.
/* For mmaped page **/
struct list* mmaped_list;
struct list_elem mmaped_elem;
struct list_elem mmaped_elem;
struct file* mmaped_file;Add commentMore actions
struct thread* owner;여기서 끝이 아닙니다. mmap과 munmap은 syscall을 통해 이루어지므로 오랜만에 userprog / syscall.c의 내용을 수정해야합니다.
userprog / syscall.c
SYS_MMAP 과 SYS_MUNMAP
void syscall_handler(struct intr_frame *f UNUSED) 내부에 위치해있습니다.
void *sys_mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int writable, int fd, off_t offset);
void munmap(void *addr);
case SYS_MMAP:
{
void *addr = (void *)f->R.rdi;
size_t length = (size_t)f->R.rsi;
int writable = (int)f->R.rdx;
int fd = (int)f->R.r10;
off_t offset = (off_t)f->R.r8;
if(is_kernel_vaddr(addr) || is_kernel_vaddr(addr + length))
break;
f->R.rax = sys_mmap(addr, length, writable, fd, offset);
break;
}
case SYS_MUNMAP:
{
void *addr = (void *)f->R.rdi;
if(is_kernel_vaddr(addr))
break;
sys_munmap(addr);
break;
}sys_mmap 와 sys_munmap
밑에 추가적인 함수 구현은 따로 밑에 작성했습니다.
void *sys_mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int writable, int fd, off_t offset) {
if (fd < 0 || fd >= MAX_FD || thread_current()->fd_table[fd] == NULL)
return NULL;
struct file *file = thread_current()->fd_table[fd];
if (file == NULL)
return NULL;
file = file_reopen(file);
return do_mmap(addr, length, writable, file, offset);
}
void sys_munmap(void *addr) {
return do_munmap(addr);
}여기서도 트러블슈팅이 있었는데, file_reopen을 하지 않으면 미리 닫아버려서 일부 테스트가 통과되지 않습니다.
결론적으로 여기까지 하면, mmap일부 테스트가 통과해서 20개의 Fail이 나옵니다.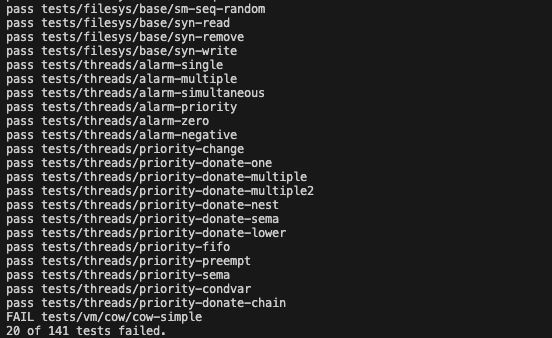
... 일부 생략
pass tests/vm/pt-grow-stack
pass tests/vm/pt-grow-bad
pass tests/vm/pt-big-stk-obj
pass tests/vm/pt-bad-addr
pass tests/vm/pt-bad-read
pass tests/vm/pt-write-code
FAIL tests/vm/pt-write-code2
FAIL tests/vm/pt-grow-stk-sc
pass tests/vm/page-linear
pass tests/vm/page-parallel
pass tests/vm/page-merge-seq
pass tests/vm/page-merge-par
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-stk
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-mm
pass tests/vm/page-shuffle
pass tests/vm/mmap-read
pass tests/vm/mmap-close
pass tests/vm/mmap-unmap
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-overlap
pass tests/vm/mmap-twice
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-write
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-ro
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-exit
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-shuffle
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd
pass tests/vm/mmap-clean
pass tests/vm/mmap-inherit
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-misalign
pass tests/vm/mmap-null
pass tests/vm/mmap-over-code
pass tests/vm/mmap-over-data
pass tests/vm/mmap-over-stk
pass tests/vm/mmap-remove
pass tests/vm/mmap-zero
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd2
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd3
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-zero-len
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-off
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-off
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-kernel
FAIL tests/vm/lazy-file
pass tests/vm/lazy-anon
FAIL tests/vm/swap-file
FAIL tests/vm/swap-anon
FAIL tests/vm/swap-iter
pass tests/vm/swap-fork
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-create
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-full
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-random
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-block
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-random
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-create
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-full
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-random
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-block
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-random
pass tests/filesys/base/syn-read
pass tests/filesys/base/syn-remove
pass tests/filesys/base/syn-write
pass tests/threads/alarm-single
pass tests/threads/alarm-multiple
pass tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
pass tests/threads/alarm-priority
pass tests/threads/alarm-zero
pass tests/threads/alarm-negative
pass tests/threads/priority-change
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-one
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
pass tests/threads/priority-fifo
pass tests/threads/priority-preempt
pass tests/threads/priority-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-condvar
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
FAIL tests/vm/cow/cow-simple
20 of 141 tests failed.발표자료도 작성해야되고, 시간이 없어서 여기까지 구현했습니다. 틈틈히 디버깅을 해봤으나, 개선되지 않았습니다. 나중에 시간이 남는다면, Fail 0을 위해 시도해보겠습니다.
Disk swap 관련된 내용을 조금이라도 진행해보고 싶었으나 못해서 너무 아쉽습니다…
지금까지 길고도 험난했던 Pintos가 끝났습니다. 앞으로는 대망의 나만의 무기만들기로 돌아오겠습니다.
'크래프톤 정글(PintOS WEEK 9 ~ 14)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Devops 운영진 티타임 (2) | 2025.06.13 |
|---|---|
| PintOS Project3: Virtual Memory (Memory Management, Anonymous Page) (2) | 2025.06.13 |
| WEEK 13 PintOS TIL(6월12일 목요일) (4) | 2025.06.13 |
| Page fault (Pintos, 발표자료) (2) | 2025.06.13 |
| 13주차 퀴즈 복습 (1) | 2025.06.13 |